Histology
Histology is the study of the microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is performed by examining a thin slice (section) of tissue under a light microscope or electron microscope. The ability to visualize or differentially identify microscopic structures is frequently enhanced through the use of histological stains. Histology is an essential tool of biology and medicine. The study of tissues bridges the gap between cell/molecular and organismal biology.
In animals there are four major tissue types: Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, and Nervous tissues. Each tissue is classified based on the location, shape, and function of the cells which comprise them.
- Epithellal Tissues
- Connective Tissues
- Muscle Tissue
- Nervous Tissue
Epithellal Tissues line or cover the surfaces of the body and hollow organs. It is rare to get a slide with just epithelial tissue on it, so focus on the outermost layer.


Squamous epithelium is comprised of thin, flatcells that adhere to one another tightly to form sheets. Function: passive transport of gases & nutrients.

![]()

Cuboidal epithelium is comprised of cube-shaped cells that often surround ducts. Function: secretion and absorption.


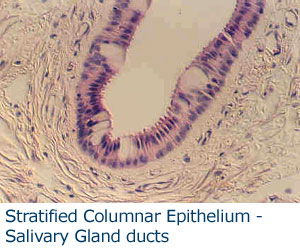
Columnar epithelium is comprised of column-shaped cells that often line absorptive surfaces (like the stomach and intestines) and regions of the respiratory tract (trachea and bronchioles) Function: absorption and secretion





Connective Tissues connect, support, and protect other tissues or structures, in addition to, storing fat, transporting substances, and helping to repair tissue damage. Unlike epithelial tissues, connective tissue cells have large intercellular spaces that are filled with matrix proteins. The connective tissues to be observed in this lab are:
Areolar connective tissue is a loose configuration of fibroblast cells suspended in a matrix of collagen, elastic, and reticular fibers. Function: anchoring, binding, and supporting other tissues. i.e. "spongy" layer between skin and muscles.
![]()

![]()

Hyaline cartilage is a form of connective tissue comprised of chondrocyte cells immersed in a matrix of collagen and elastic fibers. Occurs at the end of long bones and along the trachea. Function: structural support.

![]()

Bone is the only connective tissue with a solid matrix. Found extensively throughout the body providing structural support and protection of internal organs. Function: support, protection and storage of calcium.


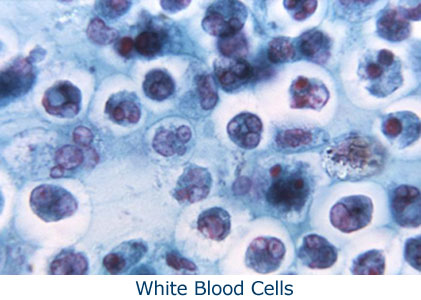
Blood is the only connective tissue with a liquid matrix. Contains red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Human red blood cells do NOT have a nucleus.- Function: carry oxygen (RBC), immune system (WBC), and clotting (platelets)
![]()

![]()
Adipose Tissue is a form of loose connective tissue comprised of fat storing adipocyte cells. The cells contain a large fat droplet, which forces the nucleus to be squeezed into a thin rim at the edge of the cell.
Muscle Tissue is specialized for the contraction or shortening of cells that are called fibers. Their main function is to move the body, or move substances along the body. They are classified by cellular appearance, location, and by whether they have voluntary or involuntary contractions.
Skeletal muscle fibers are cylindrical, multinucleated, and striated. Contraction is voluntary. Found in the muscles along the skeleton of the body. Function: locomotion

Cardiac muscle fibers are found specifically in the heart. The tissue is highly branched containing small cells with a single nucleus. The tissue has a striated appearance, and has visible intercalated disks at the junction between cells Contraction is involuntary. Function: movement of blood throughout body

Smooth muscle cells have a spindle shape and contain a single nucleus. Contraction is involuntary, and unlike the other two classes of muscle tissue do NOT have striations. Function: involuntary contraction of the bladder and digestive tract.

Nervous Tissue is specialized to conduct an electrical impulse to communicated and integrate several functions and parts of the body. Nervous tissue is comprised of neurons and the neuroglia cells that support them.
Neurons: highly branched cell that contains a central cell body (soma) multiple dendrite extensions for receiving signals from surrounding cells and a single axon for transmitting signals to downstream cells.


